in2Dredging (i2D) releases a new series of online tutorials whilst launching version 1.2 of Pumps ‘n Pipeline (PnP). PnP version 1.1 was launched nine months ago and received significant international attention. Feedback from this first release has now been incorporated into PnP v1.2, which includes new capabilities that have been thoroughly tested. In addition, PnP’s Help documentation has been revised and updated.
Although i2D’s Quality Certification is currently a work in progress, i2D nonetheless applies strict internal procedures that ensure the quality of their dredging tools. As PnP users base their estimates on our tools to ensure the competitiveness of their tenders and that any awarded projects are profitable, i2D places paramount importance in developing tools that provide the PnP User Community and our clients reliable results.
PnP’s latest features are explained in a series of new tutorial videos available on i2D’s PnP webpage. The tutorials are designed to help dredging professionals to optimise the production of their dredging equipment and to improve the accuracy of their estimates. A summary of what is covered in each new tutorial is provided below.
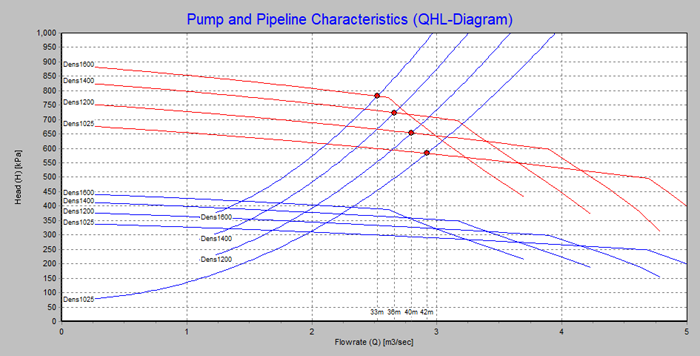
Optimise Rainbow Nozzle Diameter
As the nozzle diameter is a significant restriction in the discharge pipeline when rainbowing, determining the optimal nozzle diameter is vital and involves balancing the maximal unloading production with the minimum range of the rainbow beam.
In this tutorial, we explain how to determine the optimal nozzle diameter using the Pump and Pipeline Characteristics graph (see example below) generated by PnP v1.2
Underwater Pump in Shallow Water Depth
An underwater pump usually has an almost unlimited suction production at reasonable water depths. However, in shallow water depths the vacuum could limit production. This tutorial explains how PnP v1.2’s new Underwater Pump feature allows estimators to readily identify any significant production limitations that may occur when dredging the top soil layers.
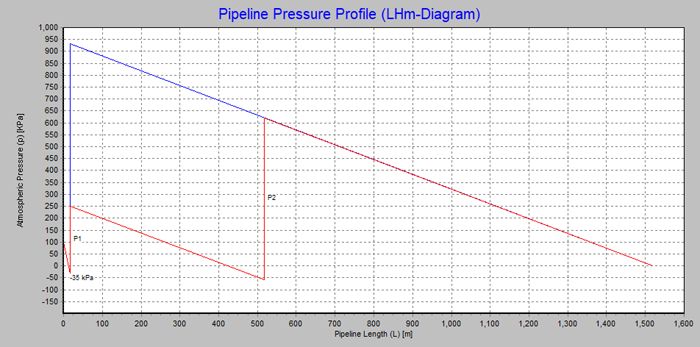
Booster stations are necessary to enable the pumping of mixtures over long distances and reduce to a more competitive unit rate the cost per cubic metre.
This video tutorial explains how PnP’s Pipeline Pressure Profile graph, (see example in Figure 2 below), is key in supporting you to optimally position a booster pump. In addition, the tutorial explains the pre-set ranges of possible booster locations and booster specifications that come with PnP v1.2 and aspects that need to be considered when positioning a booster pump.
Finally, PnP v1.2 can help you incorporate the risk of pumping clay balls in your estimate. Clay soils with both a high liquid limit and high consistency index, for example, will not dissolve during hydraulic transport, thus forming clay balls in the pipeline. PnP’s results show clay balls’ dramatic effect on discharge production and the significant impact this has on both schedules and budgets.
Interested? PnP v1.2 is available for purchase on the Pumps ‘n Pipeline webpage. As well as the traditional Single User license available until now, you can now also purchase an Annual Single User license, which is only a third of the Single User license’s price.
